What is “warm edge spacer bar”?
Materials such as aluminium, steel, stainless steel and a wide range of plastics are used for the production of distance profiles. Not all distance profiles made from those materials and their combinations can be called warm edge spacer bars.
A distance spacer bar with improved thermal properties, commonly referred to as a “warm edge spacer bar”, must comply with the condition specified in the PN-EN ISO 10077-1 standard, annexe E:
Σ (d x λ) ≤ 0,007 W/K
where:
d – spacer bar wall thickness expressed in metres
λ – spacer bar material thermal conductivity in W/(mK)
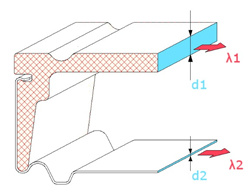
The Chromatech Ultra spacer bar cross section diagram
This pattern may be interpreted as the sum of all heat flow paths (presented on the diagram as red arrows) parallel to the main direction of the heat flow. If the value of this stream does not exceed the permissible value, we may refer to it as a “warm edge spacer bar”.
| Profile type | Chromatech Ultra | Chromatech Plus | Chromatech | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | stainless steel | PVC | stainless steel | stainless steel |
| Wall thickness [m] | 0,0001 | 0,0009 | 0,00015 | 0,00018 |
| Thermal conductivity [W/mK] | 15 | 0,17 | 15 | 15 |
| ∑ sum | 0,001653 | 0,0045 | 0,0054 | |
| “Warm edge spacer bar” condition Σ ≤ 0,007 | COMPLIANT | COMPLIANT | COMPLIANT | |
The above table presents calculations confirming the increased thermal properties of the Chromatech Ultra, Chromatech Plus and Chromatech profiles. A standard profile made from aluminium does not comply with the conditions of the standard.



